支原体污染的特点及检验(2)
互联网
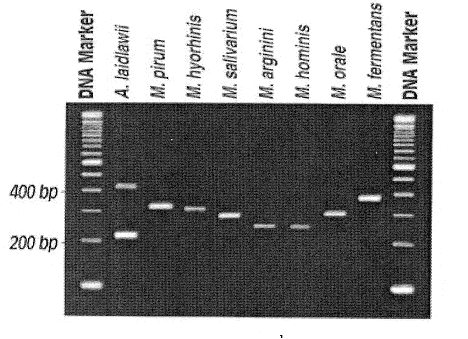
污染测试--支原体 :
PCR方法原理:
利用具特殊专一性之primers,经由PCR反应来复制mycoplasma DNA。所用之primers来自mycoplasma之conserved 16S-23S rRNA序列,由于此段spacer之序列依mycoplsma种类不同而不同,因此可依所复制之DNA大小及其restriction fragment大小差异来作侦测与鉴定。
特点:灵敏(e.g. 0.1~1.6 CFU / 5 ul sample) 与快速(一天)。可侦测不易培养之mycoplasma (e.g. M. hyorhinis)。不需培养mycoplasma作为正反应对照组,避免可能之污染。
缺点︰PCR反应很灵敏,易有伪阳性结果。此方法尚在评估中,故结果仅作为参考和内部品管之一部份。
材料与设备:
ATCC mycoplasma detection kit:可作50~100 reactions.
提供1st stage primer mixture与2nd stage primer mixture
positive control DNA (A. laidlawii ; M. pirum)
PCR reagents :
Taq polymerase ( 5 U / ul )
dNTP( dGTP, dCTP, dTTP, dATP, 1.25 mM each )
10x PCR buffer (with 1.5mM MgCl2)
25mM MgCl2
sterile ddH2O
Machine / Equipment:
PCR thermal cycler
agarose电泳设备
DNA电泳胶体观察设备
无菌PCR反应管
无菌1.5 ml微量离心管
无菌2ul, 20ul, 200ul, 1000ul Tips/ Pipetmans
方法:
此PCR反应是一种nested PCR,包括2阶段PCR反应,1st stage PCR结束后,取其反应物作2nd stage PCR,然后取2nd PCR产物作agarose gel electrophoresis,依DNA band之有无及片段大小来分析结果。
结果:使用UV light观察,并照相记录。
方法:
此PCR反应是一种nested PCR,包括2阶段PCR反应,1st stage PCR结束后,取其反应物作2nd stage PCR,然后取2nd PCR产物作agarose gel electrophoresis,依DNA band之有无及片段大小来分析结果。
结果:使用UV light观察,并照相记录。
方法再详尽点:
3.1 1st stage PCR reaction(total volume 25 ul):
3.1.1 测试样品 ( 2 ul / each )
3.1.1.1 直接取样测试细胞之培养液。
3.1.1.2 Positive control : mycoplasma DNA ( A. laidlawii ; M. pirum )
3.1.1.3 Negative control : ddH2O
3.1.2 Reaction mixture ( 23 ul / each )
3.1.2.1 10x PCR buffer (含1.5 mM MgCl2 ) 2.5 ul
3.1.2.2 1st stage primer mixture 0.5 ul
3.1.2.3 dNTP ( 1.25 mM each ) 1.0 l
3.1.2.4 MgCl2 ( 25 mM ) 0.5 ul
3.1.2.5 Taq DNA polymerase ( 5 U/ul ) 0.1 ul
3.1.2.6 ddH2O 18.4 ul
3.1.3 PCR program ( 1st PCR与2 nd PCR相同):使用PCR thermal cycler
3.1.3.1 step 1 : denaturation: 94 ℃ 30 sec
3.1.3.2 step 2 : denaturation: 94 ℃ 30 sec
3.1.3.3 step 3 : annealing: 55 ℃ 2 min
3.1.3.4 step 4 : extension: 72 ℃ 2 min
3.1.3.5 重复3.1.3.2至3.1.3.4步骤30 cycles
3.1.3.6 step 5 : final extension 72 ℃ 5 min
3.2 2 nd stage PCR reaction(total volume 25 ul)
3.2.1 测试样品:1st stage PCR product(1 ul / each)。
3.2.2 Reaction mixture ( 24 ul / each )
3.3.2.1 10x PCR buffer (含1.5 mM MgCl2 ) 2.5 ul
3.3.2.2 2 nd stage primer mixture 0.5 ul
3.3.2.3 dNTP ( 1.25 mM each ) 1.0 ul
3.3.2.4 MgCl2 ( 25 mM ) 0.5 ul
3.3.2.5 Taq DNA polymerase ( 5U/ul ) 0.1 ul
3.3.2.6 ddH2O 19.4 ul
3.2.3 PCR program同3.1.3;使用PCR thermal cycler
4.0 胶片电泳分析
4.1 胶片 (2.0%) 置备: 将2 g agarose溶于100 ml ( 1x ) TAE buffer。
4.2 电泳液:(1x) TAE buffer(Tris-acetate/EDTA electropheresis buffer)
4.3 选择100~500 bp DNA size Marker:取100 bp ladder Marker 5 ul ( 25 ng/ul )
4.4 取10 ul 2 nd stage PCR产物分析,各加入2 ul ( 6x ) loading dye。
4.5 进行电泳分离100V, 25 min。
4.6 胶片染色:ethidium bromide染色10 min,H2O退染10mim。(EtBr为致癌物质,请戴手套并小心操作)
4.7 结果:使用UV light观察,并照相记录。
Figure 1 : Agarose gel electrophoresis of the 2nd -stage PCR Products from eight commonly encountered Mycoplasma and A. laidlawii Species. ( from ATCC mycoplasma detection kit)
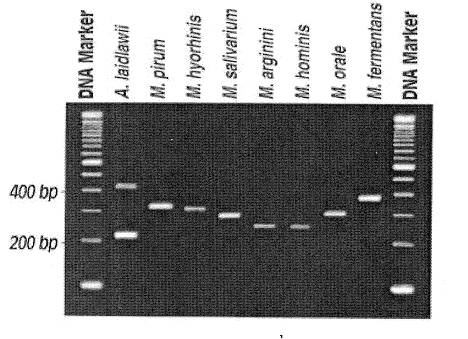
Table 1 : Variations of restriction fragment lengths of the 16S-23S rRNA intergenic spacer regions of commonly encountered species of mycoplasma. (from ATCC mycoplasma detection kit)
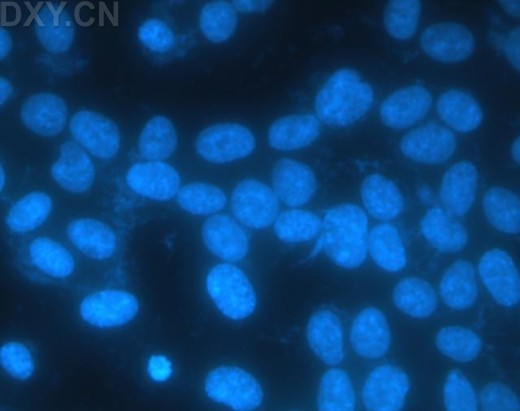
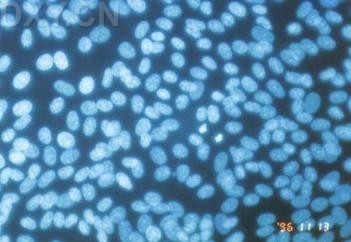
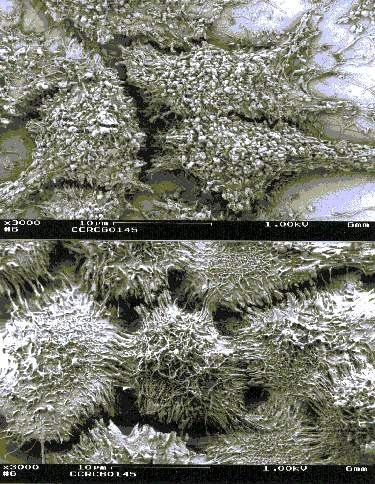
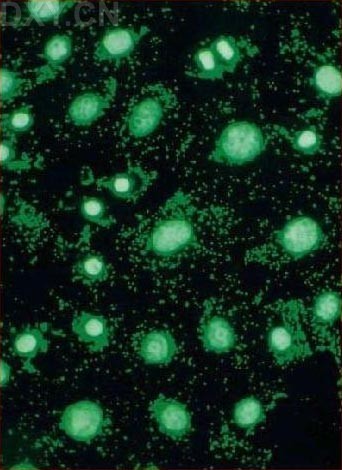
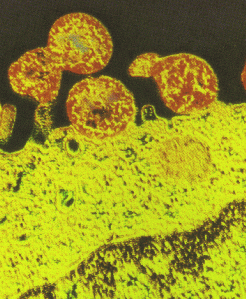
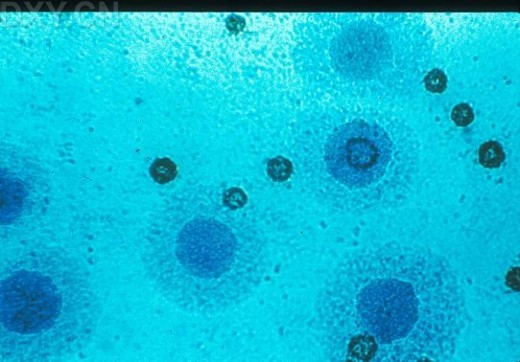
_No_restriction_site~Kbr_~H~M *_When_a_polyacrylamide_gel_is_used_for_the_resolution_of_amplified_DNA_products~E_a_double~Fband_product_with_one_bp_difference_may_be_observed_for_M._hominis._This_feature_can_serve_as_a_good_indicator_for_differentiated_M._hominis_from_M._arginini~E_which_only_produces_a_single~Fband_DNA_product.~K~Hp~M~1~Kp~M~Kimg_src~L~4https~I~H~Himg1.dxycdn.com~H2021~H1223~H350~H4940025748684632253~F68.jpg~4_width~L~4520~4_height~L~4283~4_~H~M~K~Hp~M~1~Kp~M网友“zllxash”提供支原体污染的细胞在光学显微镜下的照片:如下

Protocol:Detection of Mycoplasma by Culture
1. Inoculate 2 agar plates with 0.1ml of test sample.
2. Inoculate 1 agar plate with 100cfu M. pneumoniae.
3. Inoculate 1 agar plate with 100cfu M. orale.
4. Leave 1 agar plate un-inoculated as a negative control.
5. Inoculate 1 broth with 0.2 ml of test sample.
6. Inoculate 1 broth with 100cfu M. pneumoniae.
7. Inoculate 1 broth with 100cfu M. orale.
8. Leave 1 agar plate un-inoculated as a negative control.
9. Incubate agar plates anaerobically for 14 days at 37°C using a gas jar with anaerobic gas
pak and catalyst.
10. Incubate broths aerobically for 14 days at 37°C.
11. Between 3 and 7 days and 10 and 14 days incubation, subculture 0.1 ml of test broth onto
an agar plate and incubate plate anaerobically as above.
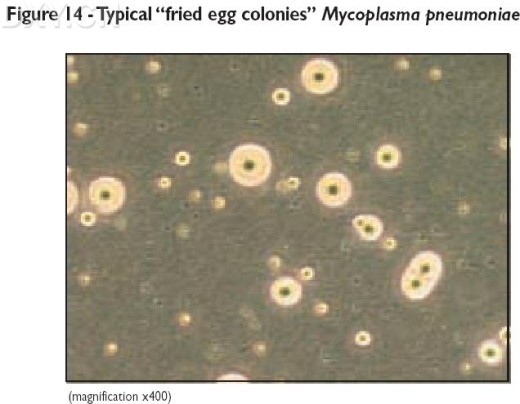
12. Observe agar plates after 14 days incubation at x300 magnification using an inverted
microscope for the presence of mycoplasma colonies (see Figure 14).
Criteria for a Valid Result
All positive control agar plates and broths show evidence of mycoplasma by typical colony
formation on agar plates and usually a colour change in broths.
All negative control agar plates and broths show no evidence of mycoplasma.
Criteria for a Positive Result
Test agar plates infected with mycoplasma show typical colony formation.
Criteria for a Negative Result
The test agar plates show no evidence of mycoplasma.
Notes
1. Mycoplasma colonies have a typical colony formation commonly described as “fried egg”
(See Figure 8) due to the opaque granular central zone of growth penetrating the agar
surrounded by a flat translucent peripheral zone on the surface. However in many cases
only the control zone will be visible.
2. Positive controls may be included at a concentration to give 100 colony-forming units.
These controls should obviously be handled in a laboratory remote from the main tissue
culture laboratory.
3. Control organisms (M. pneumoniae, and M. orale) are available from National Collection of
Type Cultures (UK).
4. Mycoplasma pneumoniae is a potential pathogen and must be handled in a class II
microbiological safety cabinet operating to ACDP Category 2 Conditions.
5. This test procedure should be carried out in a microbiology laboratory away from the cell
culture laboratory.
All from<<Cell Culture Cell Culture Fundamental Techniques in>>------Sigma