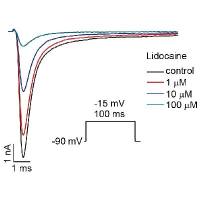
Basic Theoretical Principles--膜片钳基本理论
互联网
1170
This chapter deals with the combination of cell anatomical features and
physical and chemical properties of the cell environment that contribute to
the physiology of ion transport across the cell membrane. Starting from
the relevant properties of the cell membrane and its intracellular and
extracellular medium, we will move towards the introduction of some
electronic principles and their application to this system, and end the
chapter with electronic representations of cell membranes under a range of
electrophysiological recording conditions. Understanding of the latter is
absolutely essential for electrophysiological experimentation and data
interpretation.……
2 Basic Theoretical Principles 5
2.1 Introduction to Membrane Biology 5
2.1.1 The plasma membrane and its ionic environment 5
2.1.2 Electrochemical gradients and the Nernst equation 7
2.1.3 Maintenance of ion gradients and the membrane potential 8
2.1.4 Ion channels 11
2.2 Electrical Properties of the Cell Membrane 13
2.2.1 Driving force and membrane resistance 13
2.2.2 Membrane capacitance 15
2.2.3 Consequences of membrane capacitance 16
2.2.4 An electronic model of the plasma membrane 17
2.3 Recording Modes and their Equivalent Circuits 18
2.3.1 The basics of equivalent circuits 18
2.3.2 Intracellular recording 22
2.3.3 Voltage clamp and current clamp 28
2.3.4 Introduction to patch clamp configurations 30
2.3.5 The equivalent circuit for the cell-attached patch configuration 35
2.3.6 The equivalent circuit for the whole-cell configuration 39
2.3.7 The equivalent circuit for the excised patch configurations 40 <center> <p> </p> </center>
上一篇:膜片钳实验所需器材物品 下一篇:Single-channel Protocols and Data Analysis