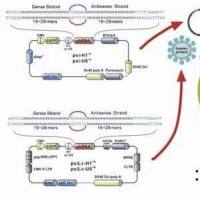
通过自杀质粒同源重组构建细菌突变株
互联网
自杀性质粒载体:一般用于基因突变。将突变的目的基因克隆到自杀性质粒载体上,通过接合等使其进入宿主,由于在宿主菌中不存在复制基因启始所需的复制蛋白(如Pi蛋白等),其无法复制,在外界选择性压力的作用下,自杀性质粒载体所携带的突变基因就与宿主染色体上的野生型发生基因发生二次同源重组,产生了带有突变的突变株;而质粒载体自身由于自杀性特性连同染色体上原有的野生型基因一起随着细菌的传代从菌体内消失。至于一次重组的突变株,可借助质粒上的某些选择基因(如sacB,sucrose敏感)筛除。
整合载体:将目的基因克隆于质粒载体上,进而整合到宿主染色体,是克服质粒不稳定性的一个有效途径。
一、关于载体
自杀性质粒载体完全可与自己构建,只要保证两点:
(一)自杀性质粒载体不能在你的宿主菌里进行复制,也就是说载体上不能有能在宿主菌中复制的复制子。
自杀性质粒载体不能在你的宿主菌里进行复制,否则会导致细菌染色体突变株的构建失败。但是在构建时,要注意以下方面:
1、在制备质粒载体和DNA插入片断时:2ug 5kb大小的线状DNA大约含有1.4poml/L5'末端磷酸。5‘突出端脱磷需要CIP0.01u/pmolDNA末端,平端或凹陷脱磷需CIP0.5u/pmolDNA末端。
2、连接质粒载体和DNA插入片断时:
(1)初次实验的可以建立几种不同的连接体系,比如插入片段与载体分子数比率可以为3:1,1:1,或1:3。
(2)可以尝试三种温度和时间的连接如4度,过夜;15度,4-6小时;25度,1小时。
3、细菌转化和筛选时:
(1)阳性对照:如果是感受态细胞,-80度储存的在5-6周后,转化率低。可用一已知标准闭环质粒鉴定感受态细胞的转化能力。
(2)阴性对照:用无DNA转化物的感受态细菌铺板,如果有菌落生长,说明其中抗生素浓度不够,或是感受态污染
(二)筛选标记
二、园友们的经验与建议
1、一般不需要有能诱导表达的重组酶基因来进行有效地同源重组。除非你的菌株是重组缺限型的,这另当别论。当然,在做自杀性质粒是需要考虑交换臂的长度,臂越长突变菌株越容易得到,筛先的工作量越少。一般,在交换的双臂保证有1kb左右的同源序列,可提高其交换效率。
2、Q:如果我想构建枯草芽胞杆菌的某个基因的突变株,(1)在体外将该基因进行突变;(2)在该突变因两端接上与染色体上该基因两端相同的核苷酸序列;(3)将该DNA片段重组入某大肠杆菌的质粒中;(4)将重组质粒线性化;(5)将线性化的质粒电转化至枯草杆菌;筛选重组子..通过上述6个步骤是否能通过同源重组完成枯草杆菌突变株的构建?(园友qzh21sohu)
A:(1)自杀质粒构建好后,不必线性化,可直接转入受体菌。
(2)按这6个步骤可以得到阳性克隆,但是你无法筛选,因为我没有在你的步骤中发现筛选标记(如抗生素抗性),一般这个筛选标记是在要突变的基因中间的。不过如果你不是基因失活,而只是点突变,那就不能将筛选标记放在突变基因中间,而应该与它紧邻,在突变基因和筛选标记两端加上相应的同源序列(1kb左右)。不过这样还有一个问题,就是你要突变的基因是单顺反子还是多顺反子,如果是多顺反子,那它所处的位置怎样?因为你要考虑不影响到其他基因的转录与翻译。请仔细检查。
(3)不同的菌要用不同的自杀质粒,因为自杀质粒是因其不能在受体菌中复制而得名的。不过你要先试一下这个质粒在芽孢杆菌中能否复制。
(4)在网上查查相关文献就好了,肯定有实验步骤。我们都是这样做的。
3、不是什么菌都可以做成高效率的感受态的。自杀载体如果没有mob位点,该用什么方法导入(结合)到受体菌中呢?园友wuji建议一种方法:噬菌体转导。我师妹就是用Bacteriophage P22往Salmonella中导入该质粒。
4、园友wuji提供的资料与建议
马里兰大学的pCVD442图谱:

Propagation of the plasmid
Plasmid pCVD442 and its derivatives can only grow in strains that have the pir gene encoding the Pi protein, which is necessary for replication of R6K plasmids. The pir gene is usually supplied by a lambda lysogen. Such strains include DH5alpha-lambdapir, SY327-lambdapir, SM10-lambdapir, and S17-lambdapir. The last two strains supply the tra genes for efficient conjugation.
Cloning into pCVD442
Cloning in pCVD442 may not be as effecient as cloning in other vectors. Plasmid pCVD442 has only a few unique sites for cloning (see above). Additionally, transformation of pir containing strains might not be as efficient as is transformation of other strains. When we have difficulty cloning into this plasmid, we sometimes create a hybrid plasmid by joining the plasmid containing the allele we wish to clone to the suicide vector with pCVD442. If the plasmid containing the desired allele does not encode ampicillin resistance, one can transform a high efficiency strain and select for ampicillin resistance. Since pCVD442 is unable to grow in a strain that lacks pir, the only ampicillin resistant strains that arise contain the hybrid plasmid. After confirming the orientation, we excise the origin of replication of the original vector and transform DH5alpha-lambdapir. Since this is an intramolecular ligation, it is highly efficient.
It is important to have sufficient flanking DNA around the altered allele to allow recombination on both sides. It is ideal to have greater than 1 kb on either side. Having equal amounts of DNA on each side is also important. Recombination is more likely to occur on the side with longer flanking DNA. Since allelic exchange requires recombination first on one side and then on the other, it is important to have equal lengths on each side. One can get away with less flanking DNA and with unequal amounts when one is using an allele that has a selectable marker.
Tranferring the suicide vector into the host strain; selecting for the first recombination event
Plasmid pCVD442 containing the allele of inerest can be introduced into the parental strain by a variety of methods including electroporation, direct conjugation from a strain that carries tra functions, or triparental conjugation along with a strain that carries a broad host-range RP4 type plasmid.
Selection for loss of the suicide vector
Once a partial merodipoid strain containing the integrated suicide vector has been obtained, the next step is a second recombination event that results in loss of the suicide vector and one of the alleles. To select for this event we dilute an overnight LB + ampcillin culture 10-6 in LB without ampicillin and grow until the culture becomes turbid. Serial dilutions are then plated on LB plates and on plates that contain modified LB that has no NaCl and has 5% sucrose. These plates are incubated overnight at 30oC. Suprisingly, the difference in the number of colonies on the plates containing and lacking sucrose is usually only ~10-fold, but most of the sucrose-resistant colonies are also ampicillin sensitive, indicating loss of the suicide vector. These colonies can then be checked by Southern blot or PCR to determine whether they have retained the wild type or the mutated allele.
感谢【求助】自杀性质粒 [精华] 帖的各位园友,由于参与该贴讨论的园友众多,在此不一一列举。